Enhancement-mode MOSFET: Depletion-mode MOSFET: The difference being the highlighted part below. Three separate lines means enhancement-mode (left) and one solid line means depletion mode (right). So, my question: Is this the only way to tell which is which, or is there a quicker way to tell (by markings on the device maybe?). Dealing with depletion-mode MOSFETs will be straightforward. A few characteristics that may be a bit confusing are: 1. Drain saturation current - IDSS With an enhancement-mode MOSFET this is a leakage current. With a depletion-mode MOSFET it is the maximum limiting. MOSFET stands for Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistor or Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor. This is also called as IGFET meaning Insulated Gate Field Effect Transistor. The FET is operated in both depletion and enhancement modes of operation. The following figure shows how a practical MOSFET looks like.
There are two types of MOSFETS: depletion-type MOSFETs and enhancement-type MOSFETs.
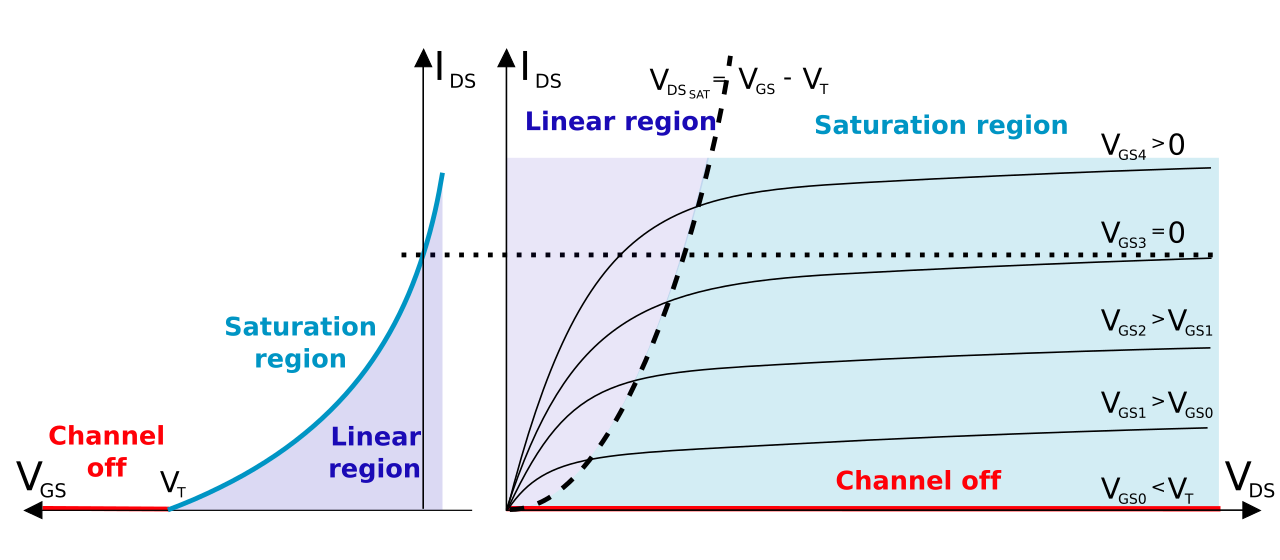
Enhancement-type MOSFETS are MOSFETs that are normally off. When you connect an enhancement-type MOSFET, no current flows from drain to source when no voltage is applied to its gate. This is why it is called a normally off device.There is no current flow without a gate voltage.
However, if a voltage is applied to the gate lead of the MOSFET, the drain-source channel becomesless resistive. As the gate-source voltage increases more and more, the current flowing from drain to source increasesmore and more, until maximum current is flowing from drain to source.
An enhancement-type MOSFET is so named an enhancement device, because as the voltage to the gate increases, the current increases more and more, until at maximum level.
An enhancement-type MOSFET behaves very similar in action to a bipolar junction transistor.
The other type of MOSFET, a depletion-type MOSFET, has the complete opposite behavior. Depletion MOSFETsare normally on devices. They conduct current at maximum level when there is no voltage applied to the gate lead. with a depletion-type MOSFET, as you increase the gate-source voltage, the drain-source channel of the transistor becomes more resistive and the current flowing from drain to source decreases, and if the gate-source voltage reachesthe cutoff level, the current completely ceases to flow.
Mosfet Enhancement And Depletion Mode
Difference between enhancement and depletion type mosfet
Depletion mode MOSFET is normally turned on at zero gate voltage. Such devices are used as load resistors.
MOSFETs with enhancement modes are the common switching elements in most MOSs. These devices are deactivated at zero gate voltage and can be switched on by powering the gate.
In field effect transistors (FET), exhaust mode and amplification mode are two major types of transistor, corresponding to whether the transistor is in the ON or OFF state at zero gate-source voltage.
Enhancement MOSFET
MOSFETs with enhancement modes can be switched on by powering the gate either higher than the source voltage for NMOS or lower than the source voltage for the PMOS.
In most circuits, this means that pulling a MOSFET gate voltage into the leakage boost mode becomes ON.
For N-type discharging devices, the threshold voltage could be about -3 V, so it could be stopped by dragging the 3 V negative gate (leakage by comparison is more positive than the NMOS source).
In PMOS, polarities are reversed.
The mode can be determined by the voltage threshold sign (gate voltage versus source voltage at the point where only a layer inversion is formed in the channel):
- For a N-type FET, modulation devices have positive and depleted thresholds – modulated devices have negative thresholds;
- For a P-type FET, positive mode to improve negative mode, depletion.
Depletion MOSFET

Junction-effect junction transistors (JFET) are the depletion mode because the gate junction would transmit the bias if the gate was taken more than a bit from the source to the drain voltage.
Such devices are used in gallium-arsenide and germanium chips, where it is difficult to make an oxide isolator.
Difference Between Depletion And Enhancement Mode Mosfet
Figure describes the construction of MOSFET type of exhaustion. Also note the MOSFET circuit type N exhaust channel symbol.
Due to its construction, it offers very high entry strength (approximately 1010 to 1015). Significant current flows for VDS data at 0 volts VGS.
Mosfet Depletion Vs Enhancement Mode
When the gate (ie, a capacitor plate) is made positive, the channel (i.e., the other capacitor plate) will have a positive charge induced therein.
This will lead to the depletion of the major bearers (ie electrons) and therefore to the reduction in conductivity.
Difference between enhancement and depletion type mosfet in tabular form
| Sr.No. | Depletion MOSFET (D-MOSFET) | Enhancement MOSFET (E-MOSFET) |
| 1 | It is called a depletion MOSFET because of channel depletion. | It only works in enhancement mode and is therefore called Enhancement MOSFET. |
| 2 | It can be used as E-MOSFET. | It can not be used as a D-MOSFET. |
| 3 | If Vgs = 0 V, Ids flows due to Vds. | If Vgs = 0V, Ids = 0, although Vds is applied. |
| 4 | N-type semiconductors exist in the structure itself between source and drain. | There is no n-channel between source and drain. |
| 5 | Do not occur | When Vgs = Vt, the MOSFET is turned on. |
Now you know difference between enhancement and depletion mosfet.
